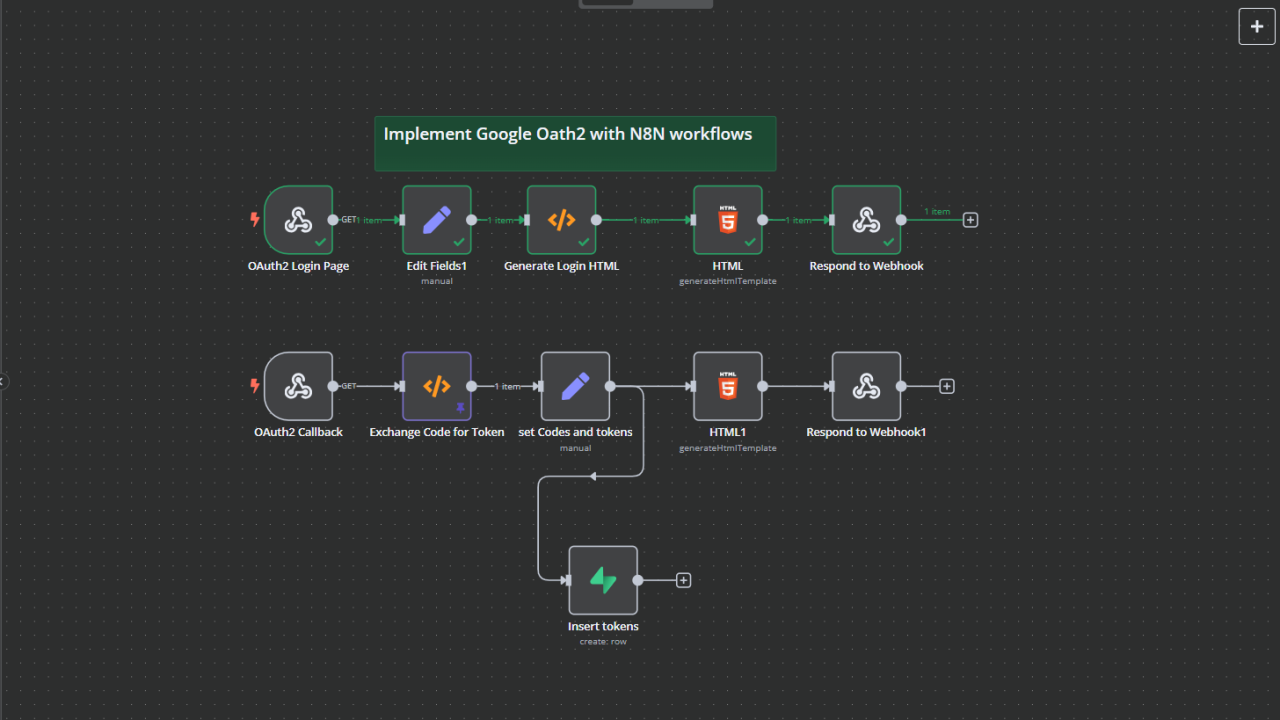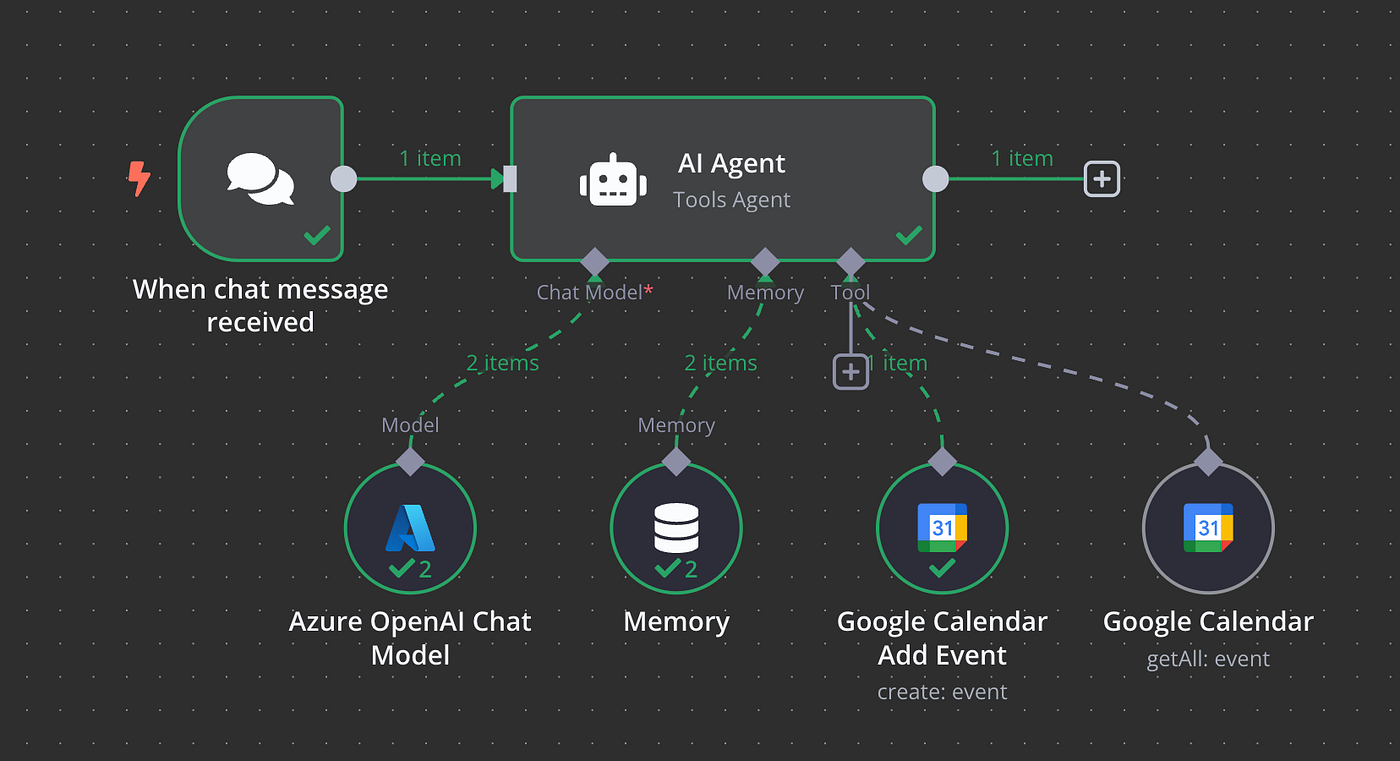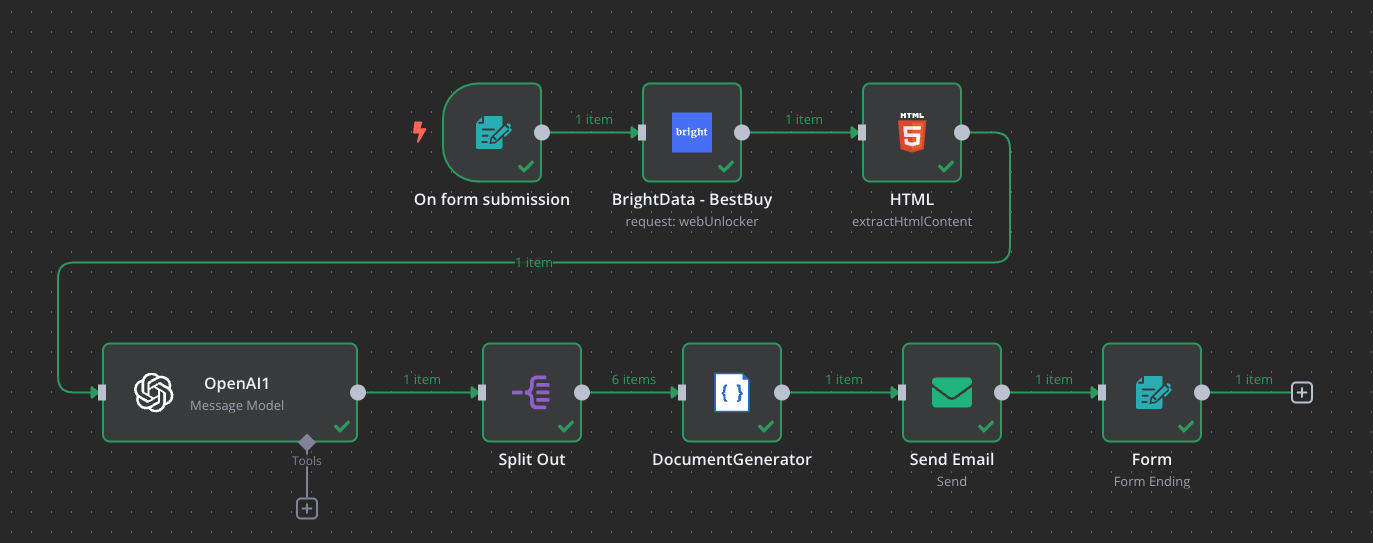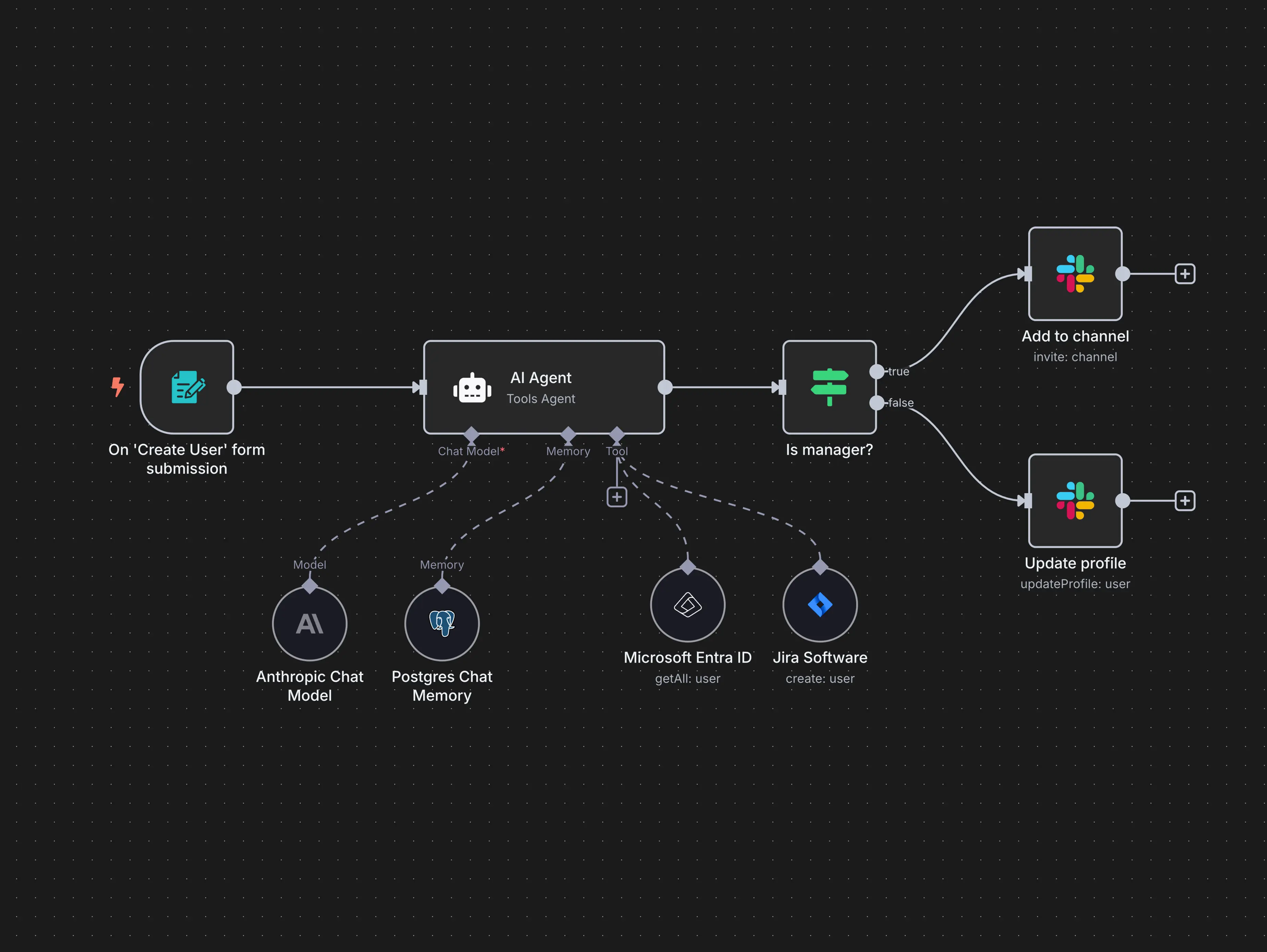
Artificial Intelligence (AI) agents are transforming how we interact with software, automate tasks, and enhance decision-making. From virtual assistants to autonomous trading bots, AI agents are at the core of the next wave of intelligent systems. In this blog, we’ll explore what AI agents are, how they work, and how to build them.
What is an AI Agent?
An AI agent is a system that can perceive its environment, process information, and take actions to achieve specific goals. Unlike traditional software, AI agents can learn from experience, adapt to new situations, and make autonomous decisions.
Examples include:
- Chatbots that provide customer support.
- Recommendation engines that suggest products or content.
- Robotics agents that perform physical tasks.
- Automation agents for workflows and data processing.
Key Components of an AI Agent
- Perception (Input Layer)
Collects data from the environment (text, images, sensors, APIs). - Reasoning/Decision-Making
Processes input using algorithms, machine learning models, or rule-based systems. - Action (Output Layer)
Executes actions, such as sending a response, triggering an API call, or moving a robot. - Learning (Feedback Loop)
Improves performance over time by analyzing outcomes.
Steps to Develop an AI Agent
- Define the Objective
Clearly state the problem the agent will solve. (e.g., “Assist customers with order tracking.”) - Select the Environment
Determine where the agent will operate (web app, mobile app, IoT device, backend service). - Choose the Framework & Tools
- LangChain, AutoGPT, CrewAI for LLM-powered agents.
- TensorFlow / PyTorch for custom ML models.
- OpenAI, Anthropic, Hugging Face APIs for language and vision capabilities.
- Design the Agent Architecture
- Input handling (APIs, user prompts).
- Processing (LLMs, ML models, rules).
- Memory (databases, vector stores like Pinecone, Weaviate, or FAISS).
- Output execution (UI updates, API calls, robotic actions).
- Integrate Memory and Context
Agents should remember previous interactions and use context for better decision-making. - Enable Autonomy and Tools
Allow agents to call APIs, fetch data, and make multi-step decisions. - Test and Iterate
Continuously refine behavior through simulation, A/B testing, and feedback.